Microscope-Assisted
Root Canal Treatment
Root Canal Treatment
Inside the tooth, there are narrow canals called root canals, which contain nerves and blood vessels known as the dental pulp.
These can become inflamed due to cavities or trauma.
If the nerve can be preserved, it is kept intact.
If not, the root canals are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected to treat the infection while preserving the tooth.
What is Root Canal Treatment?
In root canal treatment, infected nerves and bacteria are removed, and the inside of the tooth root is thoroughly cleaned and disinfected.
The root canal is then sealed with medication to prevent bacteria from re-entering.
Finally, a white non-metallic post is placed, and the tooth is restored with a crown or other restoration.
This not only improves aesthetics but also restores functionality, including proper bite alignment.
TROUBLE
Recommended for Patients with the Following Symptoms
- Tooth pain
- Deep cavities
- Discoloration of the tooth
- Localized gum swelling
- Presence of pus or foul odor
Goals of Root Canal Treatment
Frequently Asked Questions
- QHow long does the treatment take?
- AIt depends on the condition of the root canal, but usually requires several visits (about 2–4 appointments).
- QIs the treatment painful?
- ALocal anesthesia is used during treatment, so you will feel little to no pain.
After the procedure, you may experience mild discomfort, but it usually subsides within a few days.
Root Canal Treatment Case
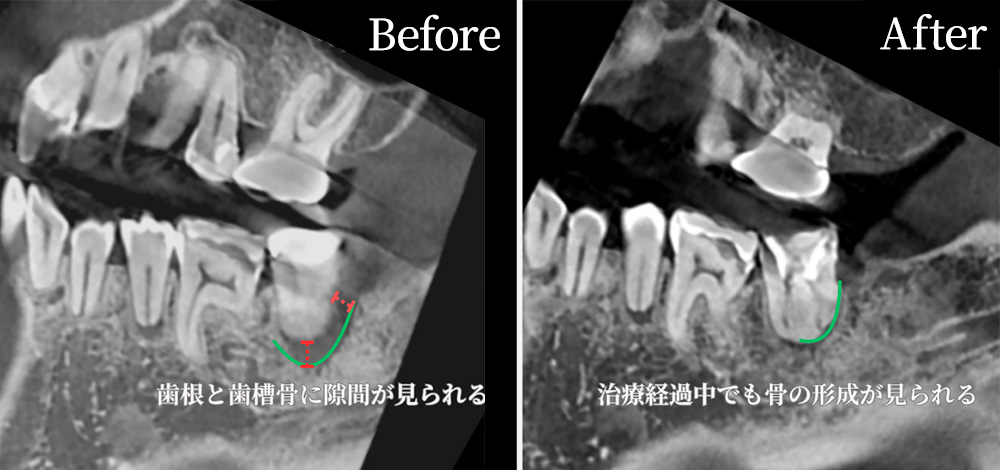
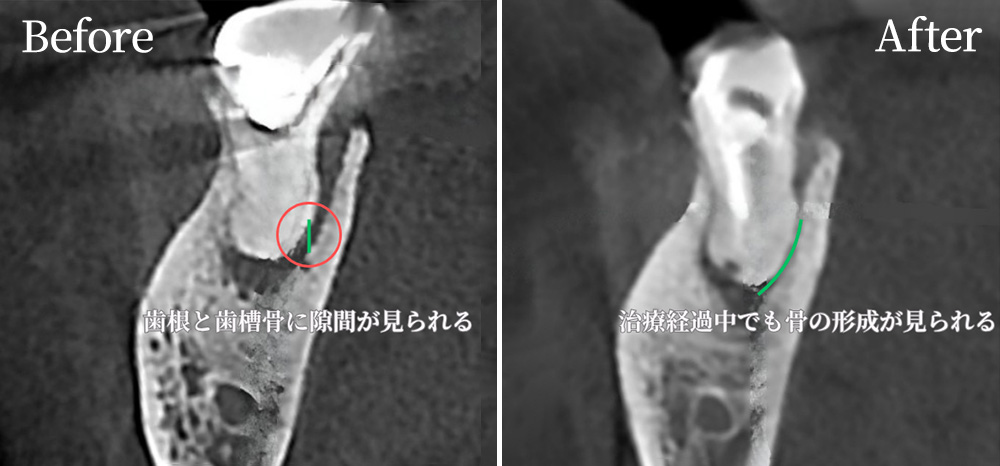
CT imaging shows traces of previous root canal treatment in one of the molars.
There is also a radiolucent area (darkened region) around the root, which may indicate past infection or chronic inflammation.
CT allows us to clearly see fine structures, root canal branches, curvatures, and any additional canals that are difficult to detect with the naked eye or conventional X-rays.
In cases like this, other clinics may recommend extraction.
At our clinic, we prioritize preserving natural teeth as much as possible, performing precise diagnosis and treatment using a dental microscope and CT imaging.